什么是装饰器模式
装饰器模式(Decorator),动态地给一个对象添加一些额外的职责,就增加功能来说,装饰器模式比生成子类更为灵活;它允许向一个现有的对象添加新的功能,同时又不改变其结构。
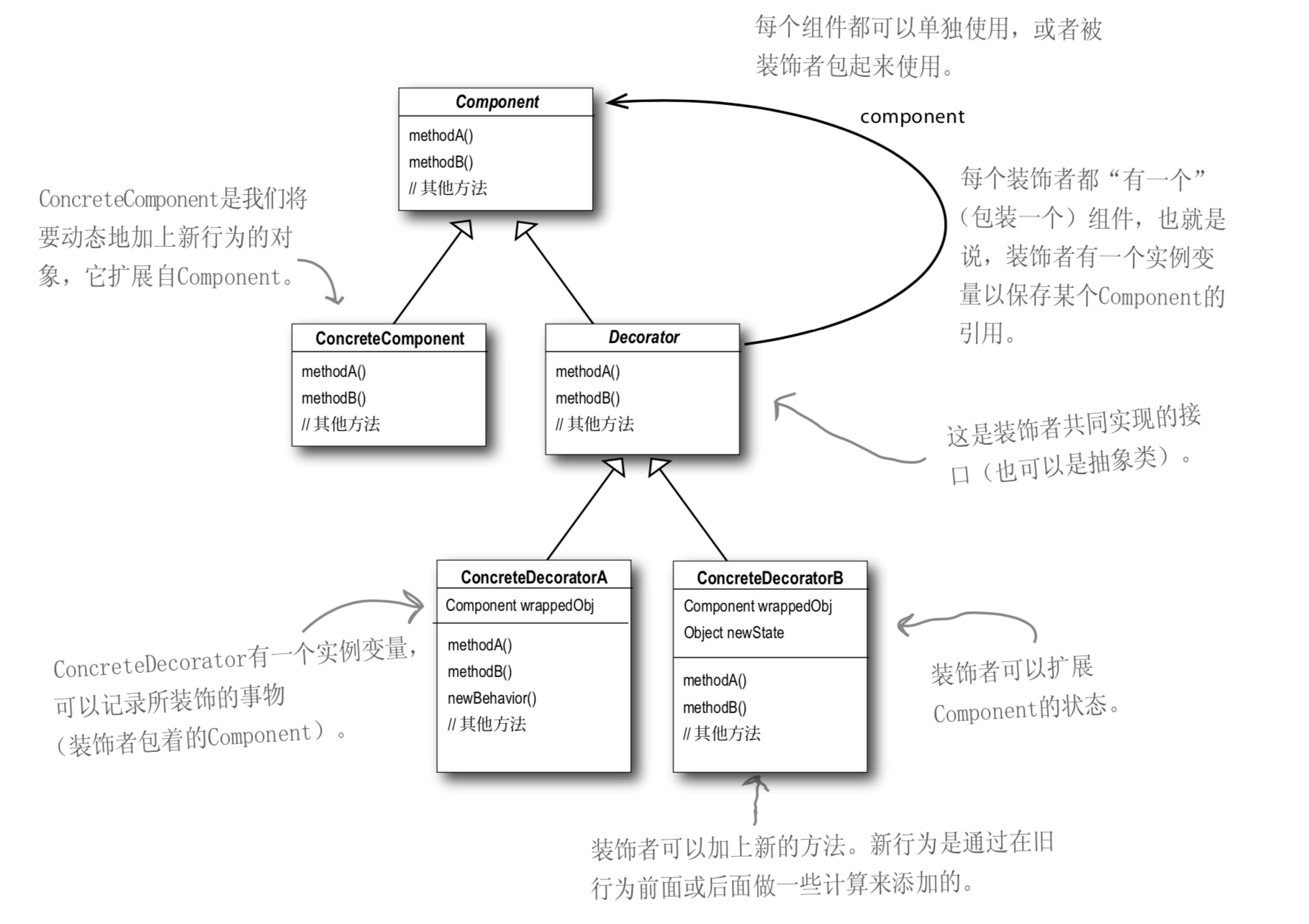
类图
Component:接口,定义一个抽象接口,真实对象和装饰对象具有相同的接口,以便动态的添加职责。
ConcreteComponent:具体的对象。
Decorator:装饰类,继承了Component,从外类来扩展Component类的功能,并且持有一个构建引用,进行请求转发。
ConcreteDecorator:具体装饰类,用于给实际对象添加职责。
代码实现
现在考虑这样一个场景,现在有一个煎饼摊,人们去买煎饼(Pancake),有些人要加火腿(Ham)的,有些人要加鸡蛋(Egg)的,有些人要加生菜(Lettuce)的,当然土豪可能有啥全给加上^_^。用上述的装饰器模式来进行编码。
定义煎饼接口IPancake
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9/**
* 定义一个煎饼接口
*/
public interface IPancake {
/**
* 定义烹饪的操作
*/
void cook();
}定义具体的煎饼Pancake
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8/**
* 具体的煎饼对象,可用其他装饰类进行动态扩展。
*/
public class Pancake implements IPancake{
public void cook() {
System.out.println("的煎饼");
}
}定义抽象装饰类PancakeDecorator
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17/**
* 实现接口的抽象装饰类,建议设置成abstract.
*/
public abstract class PancakeDecorator implements IPancake {
private IPancake pancake;
public PancakeDecorator(IPancake pancake) {
this.pancake = pancake;
}
public void cook() {
if (this.pancake != null) {
pancake.cook();
}
}
}具体装饰类EggDecorator
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18/**
* 对煎饼加鸡蛋的装饰类,继承PancakeDecorator,覆盖cook操作
*/
public class EggDecorator extends PancakeDecorator {
public EggDecorator(IPancake pancake) {
super(pancake);
}
/**
* 覆盖cook方法,加入自身的实现,并且调用父类的cook方法,也就是构造函数中
* EggDecorator(IPancake pancake),这里传入的pancake的cook操作
*/
public void cook() {
System.out.println("加了一个鸡蛋,");
super.cook();
}
}具体装饰类HamDecorator
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18/**
* 对煎饼加火腿的装饰类,继承PancakeDecorator,覆盖cook操作
*/
public class HamDecorator extends PancakeDecorator {
public HamDecorator(IPancake pancake) {
super(pancake);
}
/**
* 覆盖cook方法,加入自身的实现,并且调用父类的cook方法,也就是构造函数中
* EggDecorator(IPancake pancake),这里传入的pancake的cook操作
*/
public void cook() {
System.out.println("加了一根火腿,");
super.cook();
}
}具体装饰类LettuceDecorator
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18/**
* 对煎饼加生菜的装饰类,继承PancakeDecorator,覆盖cook操作
*/
public class LettuceDecorator extends PancakeDecorator {
public LettuceDecorator(IPancake pancake) {
super(pancake);
}
/**
* 覆盖cook方法,加入自身的实现,并且调用父类的cook方法,也就是构造函数中
* EggDecorator(IPancake pancake),这里传入的pancake的cook操作
*/
public void cook() {
System.out.println("加了一颗生菜,");
super.cook();
}
}客户端调用以及结果
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19/**
* 调用客户端
*/
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("=========我是土豪都给我加上===========");
IPancake pancake = new Pancake();
IPancake pancakeWithEgg = new EggDecorator(pancake);
IPancake pancakeWithEggAndHam = new HamDecorator(pancakeWithEgg);
IPancake panckeWithEggAndHamAndLettuce = new LettuceDecorator(pancakeWithEggAndHam);
panckeWithEggAndHamAndLettuce.cook();
System.out.println("==========我是程序猿,加两个鸡蛋补补==============");
IPancake pancake2 = new Pancake();
IPancake pancakeWithEgg2 = new EggDecorator(pancake2);
IPancake pancakeWithTwoEgg = new EggDecorator(pancakeWithEgg2);
pancakeWithTwoEgg.cook();
}
}
输出结果
1 | =========我是土豪都给我加上=========== |
四. 总结
关于装饰器模式的使用,在我看来主要有一下几点需要注意的:
* 抽象装饰器和具体被装饰的对象实现同一个接口
* 抽象装饰器里面要持有接口对象,以便请求传递
* 具体装饰器覆盖抽象装饰器方法并用super进行调用,传递请求
- 适用场景
- 扩展一个类的功能。
- 动态添加功能,动态撤销。
- 优点
- 装饰类和被装饰类都只关心自身的核心业务,实现了解耦。
- 方便动态的扩展功能,且提供了比继承更多的灵活性。
- 缺点
- 如果功能扩展过多,势必产生大量的类。
- 多层装饰比较复杂。